- Access exclusive content
- Connect with peers
- Share your expertise
- Find support resources
Click Preferences to customize your cookie settings.
Unlock your full community experience!
Demystifying NAT Traversal with VPN IPsec
- LIVEcommunity
- Discussions
- Network Security
- Next-Generation Firewall Discussions
- Demystifying NAT Traversal with VPN IPsec
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Printer Friendly Page
Demystifying NAT Traversal with VPN IPsec
- Mark as New
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
12-30-2023 08:13 AM - edited 12-30-2023 08:22 AM
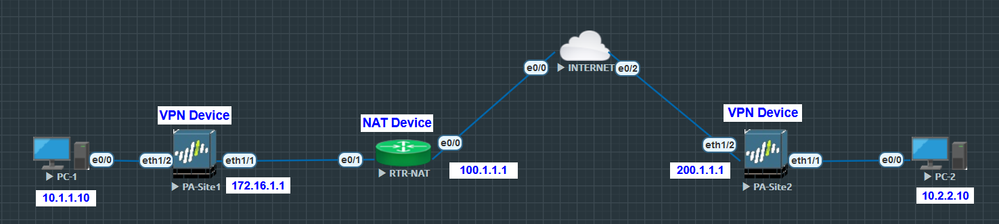
One of the biggest concepts in VPN Technologies is NAT Traversal, like NAT Traversal in VOIP deployment with SIP Protocol, the story is always inside the payload to solve the Incompatibility between NAT and IPSEC similar to the Incompatibility between SIP protocol and NAT.
IPsec uses ESP to encrypt all packet, encapsulating the L3/L4 headers within an ESP header. ESP is an IP pro tocol but there is no port number (Layer 4). This is a difference from ISAKMP which uses UDP port 500 as its UDP layer 4.
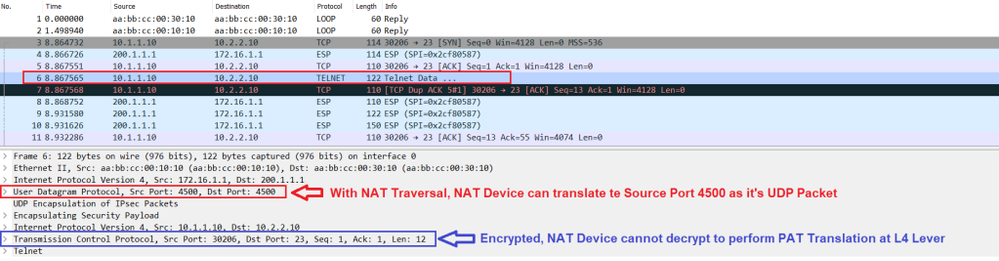
Because ESP is a protocol without ports and at the other side the L4 information the, The NAT device cannot change these encrypted headers and cannot perform PAT translation at the L4 level.
Below the telnet packet captured from PC-1 to PC-2, the Source port 30206 and the Destination Port 23 are encapsulated by ESP and both are encrypted. inside ESP after decryption at the PA-Site2.
Without NAT Traversal and new UDP Encapsulation of ESP packets with source port 4500 and destination 4500, the NAT Device cannot do anything.
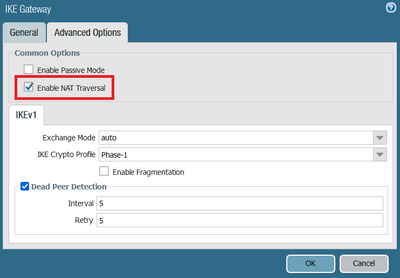
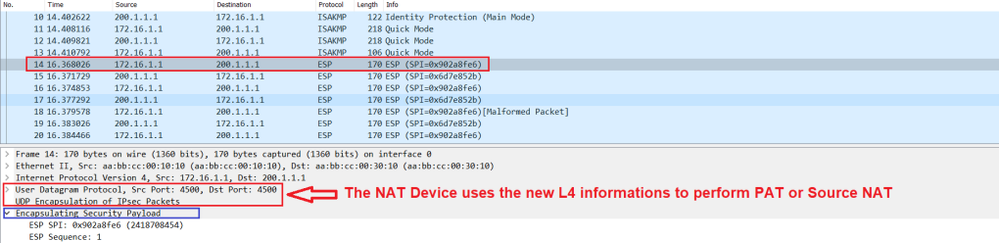
NAT and IPSec are incompatible with each other, and to solve this, NAT Traversal was developed. NAT Traversal adds a UDP header which encapsulates the IPSec ESP header. As this new UDP header is NOT encrypted and is treated as just like a normal UDP packet, the NAT device can make the required changes and process the message,
NAT Traversal performs two tasks:
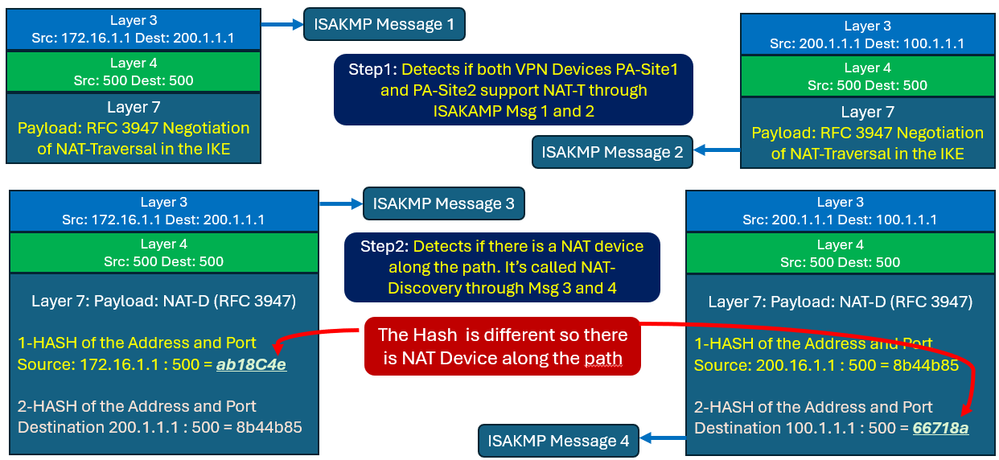
Step-1: Detects if both VPN Devices RTR-Site1 and RTR-Site2 support NAT-T
Step-2: Detects if there is a NAT device along the path. It’s called NAT-Discovery.
Step-1 is performed in ISAKMP phase 1 (Main Mode ) through the messages one and two as shown below between PA-Site1 172.16.1.1 and PA-Site-2 200.1.1.1.
If both devices support NAT-T, then NAT-Discovery is performed in ISKAMP Phase 1 through messages three and four.
How do the VPN Devices PA-Site1 and PA-Site2 detect that there is a NAT device?
The answer is NAT-D payload, the PA-Site1 device sent a NAD-ID payload, inside the NAT-ID payload there are a hash of the Source IP address and port (172.16.1.1 and 500) and a hash of the Destination IP address and port (200.1.1.1 and 500).
The PA-Site1 device (172.16.1.1) sends the following:
- A HASH of Source IP address and port (172.16.1.1 and 500): ab18C4efb950c61f568a636561764e6f
- A HASH of Destination IP address and port (200.1.1.1 and 500): 8b44b859631968ceeb26b61430014fc6
The PA-Site2 (200.1.1.1) device responds with the following:
- A HASH of Source IP address and port (200.1.1.1 and 500): 8b44b859631968ceeb26b61430014fc6
- A HASH of Destination IP address and port (100.1.1.1 and 500): 66718a3d26322b74c7de2c87fb1ff4c9
The result is that the receiving device PA-Site2 recalculates the hash based on the Destination Peer IP Address 100.1.1.1 and Port 500 which is 66718a3d26322b74c7de2c87fb1ff4c9 and compares it with the hash it received from RTR-Site1 which is ab18C4efb950c61f568a636561764e6f.
If they don’t match a NAT device exists. This is the case in our scenario, the values are different.
Now PA-Site1 and PA-Site2 agree that a NAT Device exists along the path.
Now the NAT Device is discovered, still in the IKE 1 phase 1, PA-Site1 will change the UDP port 500 to UDP port 4500 in messages five and six.
Because the NAT-T, in IKE Phase 2 (IPsec Quick Mode) encapsulates the Quick Mode (IPsec Phase 2) inside UDP 4500. After Quick Mode negociation is completed, Phase 2 is now ready to encrypt the data and ESP Packets are encapsulated inside UDP port 4500 as well, thus providing a port to be used in the NAT device to perform port address translation.
UDP encapsulation is used to hide the ESP packet behind the UDP header. So that the NAT Device processes the ESP packet as a normal UDP packet.
In other words, PA-Site1 encapsulates ESP packets inside UDP/4500 for Source and Destination Ports. After this encapsulation, NAT device can now translate the ESP packets. It will change the source port from 4500 to a random port and the source IP address from 172.16.1.1 to 100.1.1.1 and kept the destination port 4500
When a packet with source and destination port of 4500 is sent through a PAT device (from inside to outside), the PAT device will change the source port from 4500 to a random high port, while keeping the destination port of 4500.
- 1071 Views
- 0 replies
- 2 Likes
Show your appreciation!
Click Accept as Solution to acknowledge that the answer to your question has been provided.
The button appears next to the replies on topics you’ve started. The member who gave the solution and all future visitors to this topic will appreciate it!
These simple actions take just seconds of your time, but go a long way in showing appreciation for community members and the LIVEcommunity as a whole!
The LIVEcommunity thanks you for your participation!
- Palo Alto On AWS - Ipsec VPN IPSEC Site to Site connection - NAT-T - IP Mapping in VM-Series in the Public Cloud
- site to site vpn using a PA inside Azure in VM-Series in the Public Cloud
- Site to Site VPN IPsec b/w Palo Alto and Cisco with only public IP as Mgmt interface on Azure in VM-Series in the Public Cloud