- Access exclusive content
- Connect with peers
- Share your expertise
- Find support resources
Click Preferences to customize your cookie settings.
Unlock your full community experience!
NAT & its Types | U-Turn NAT | Static NAT | Dynamic IP NAT | NAPT
- LIVEcommunity
- Discussions
- Network Security
- Next-Generation Firewall Discussions
- NAT & its Types | U-Turn NAT | Static NAT | Dynamic IP NAT | NAPT
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Printer Friendly Page
NAT & its Types | U-Turn NAT | Static NAT | Dynamic IP NAT | NAPT
- Mark as New
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
08-03-2023 11:36 AM
In a series of articles from Basic to advance Network Security, as today we will explain the topics Below.
- · NAT & its types
- · U-Turn NAT.
What is NAT?
NAT means translation of IP Address. Normally everyone understands that translation from private (non-routable) to public routable IP, but actually this translation can be between Private-to-Public and Public-to-Private IP Addresses. Let’s Clarify in Details Below.
Types of NAT?
- Ø Source NAT
- Ø Destination NAT
Source NAT: In the source NAT below are two conditions
- Ø Traffic flow from LAN(Internal) to Internet (WAN) and the source private IP address will be translated.
Types of Source NAT:
Dynamic IP and Port (DIPP) OR NAPT (Network Address port translation):
In this type of Source NAT, the Translation of one-to-many IP Addresses plus different port number, for example in LAN have 10 hosts all are translating to one public IP Address with different port.
This NAT is also called interface-based NAT as all Internal LAN hosts translate to one external Public IP Address.
Dynamic IP: Dynamic translation of one-to-one means if five hosts in LAN & five public IP Addresses then all are translating to unique public IP Addresses without changing port number. If add one new host in LAN as now 6 then this host will not translate & connection dropped.
The Best Design in this case is to configure Dynamic IP & DIPP NAT.
Static Vs Dynamic IP NAT:
Types of Destination NAT:
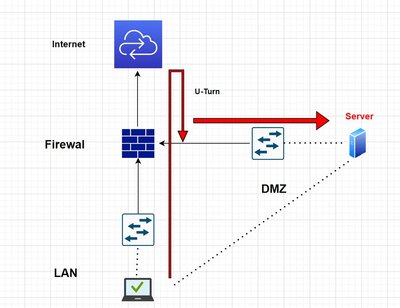
Destination U-Turn NAT:
for the complete reading below link for reference
www.readteknology.com/2023/07/nat-its-types-u-turn-nat-static-nat.html
https://www.readteknology.com/
- 5146 Views
- 0 replies
- 0 Likes
Show your appreciation!
Click Accept as Solution to acknowledge that the answer to your question has been provided.
The button appears next to the replies on topics you’ve started. The member who gave the solution and all future visitors to this topic will appreciate it!
These simple actions take just seconds of your time, but go a long way in showing appreciation for community members and the LIVEcommunity as a whole!
The LIVEcommunity thanks you for your participation!
- Request Advice – BGP Failover Route-Based IPsec VPN With WatchGuard (WG) in Next-Generation Firewall Discussions
- Announcing the Unified Incident Framework (UIF) in Strata Cloud Manager in Strata Cloud Manager
- Dynamic IP at Spoke site in PAN-OS SD-WAN Hub/Spoke topology in Next-Generation Firewall Discussions
- VPN between palo alto and Meraki with dynamic WAN ip address in Panorama Discussions
- Remote Access VPN on PPPOE dynamic ip in GlobalProtect Discussions