- Access exclusive content
- Connect with peers
- Share your expertise
- Find support resources
Click Preferences to customize your cookie settings.
Unlock your full community experience!
Aruba Access Points
- LIVEcommunity
- Tools
- HTTP Log Forwarding
- Log Forwarding Articles
- Aruba Access Points
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
on 08-08-2017 02:22 PM - edited on 10-22-2019 11:53 AM by Retired Member
Disclaimer
This document is intended as an easy example on how to leverage action oriented and selective log forwarding in PAN-OS 8.0, not as a comprehensive solution document.
Goal
This document summarizes the information and relevant steps to integrate Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation Firewalls with Aruba Instant Access Points to automatically disconnect and blacklist a device from the wireless network based on something detected by the firewall (use of an application, access to a honeypot, C&C, vulnerability exploits, etc).
This can be done with Panorama and Aruba ClearPass to apply to larger implementations, but for simplicity I used a single firewall with a single IAP.
Action-Oriented Log Forwarding using HTTP
To enable better integration between your firewall and IT infrastructure, PAN‐OS 8.0 gives you the ability to trigger an action or initiate a workflow to an external HTTP‐based service, when a log is generated on the firewall. You can now forward logs from the firewall or Panorama to an HTTP(S) destination to accomplish the following task more easily.
Send an HTTP‐based API request directly to a third‐party service to trigger an action based on the attributes in a firewall log. You can configure the firewall to work with any HTTP‐based service that exposes an API, and modify the URL, HTTP header, parameters, and the payload in the HTTP request to meet your integration needs. This capability when used with the Selective Log Forwarding Based on Log Attributes allows you to forward logs that match a defined criteria so that you can automate a workflow or an action; you do not need to rely on an external system to convert syslog messages or SNMP traps to an HTTP request.
ARUBA IAP API
ArubaOS allows you to set up customized external captive portal user management using its native XML API interface. The XML API interface allows you to create and execute user management operations seamlessly onbehalf of the clients or users. You can use the XML API interface to add, delete, authenticate, or query a user or a client.
Create an XML request with an appropriate authentication command and send it to the controller via HTTPS post. The format of the URL to send the XML request is:
https://<controller-ip/auth/command.xml
In which,
- controller-ip is the IP address of the controller that will receive the authentication request
- xmlis the XML request that contains the details of authentication.
The format of the XML API request is:
xml=<aruba command="<authentication_command>">
<options>Value</options>
...
<options>Value</options>
</aruba>
You can specify any of the following commands in the XML request:
|
Table 1 XML API Authentication Command |
|
|
Authentication Command |
Description |
|
user_add |
This command adds the user to the controllers user table. |
|
user_delete |
This command deletes the user from the controller |
|
user_authenticate |
This command will authentication the user based on the authentication rules defined in the controllers configuration. |
|
user_blacklist |
This command will block a user from connection to your network. |
|
user_query |
This command will display the current status of the user connected to your network. |
The authentication command requires certain mandatory options to successfully execute the authentication tasks. The list of all available options are:
|
Table 2 Authentication command options |
||
|
Options |
Description |
Range / Defaults |
|
ipaddr |
IP address of the user in A.B.C.D format. |
— |
|
macaddr |
MAC address of the user aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ff format. |
Enter MAC address with colon. |
|
user |
Name of the user. |
64 character string |
|
role |
Role name assigned after authenticating. |
64 character string |
|
password |
The password of the user used for authentication. |
— |
|
session_timeout |
Session time-out in minutes. User will be disconnected after this time. |
— |
|
authentication |
Authentication method used to authenticate the message and the sender. You can use any of MD5, SHA-1 or clear text methods of authentication. This option is ignored if shared secret is not configured. It is, however, mandatory if it is configured. |
— |
|
key |
This is the encoded SHA1/MD5 hash of shared secret or plaintext shared secret. This option is ignored if shared secret is not configured on the switch. The actual MD5/SHA-1 hash is 16/20 bytes and consists of binary data. It must be encoded as an ASCII based HEX string before sending. It must be present when the controller is configured with an xml-api key for the server. Encoded hash length is 32/40 bytes for MD5/SHA-1. |
|
|
version |
The version of the XML API interface available in the controller. This field is mandatory is all requests. |
Current version 1.0 |
Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation Firewall Configuration Steps
- Follow the firewall quick start guide to get a working environment where traffic from wireless users is traversing the firewall and logs are being generated.
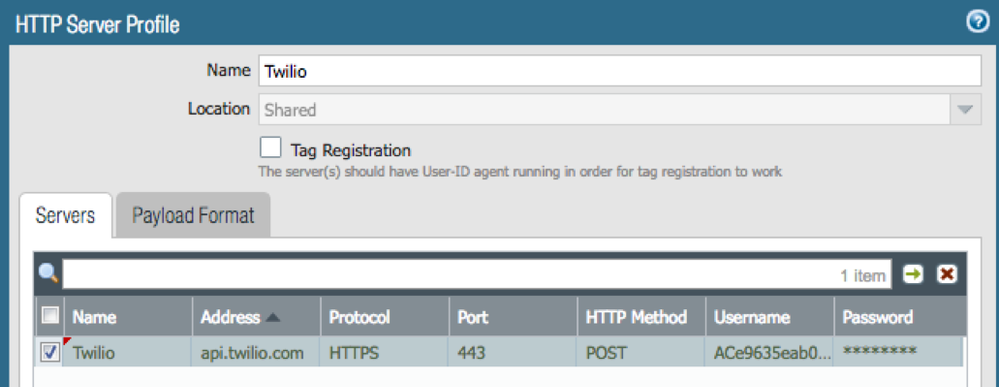
- Create an HTTP Server Profile and add the IAP IP address with protocol HTTPS, port 443 and HTTP Method POST
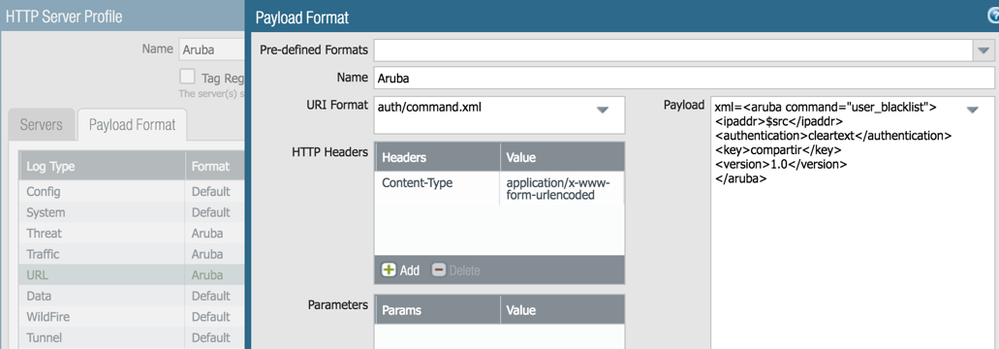
- Define the payload format for all relevant log types
xml=<aruba command="user_blacklist">
<ipaddr>$src</ipaddr>
<authentication>cleartext</authentication>
<key>shared-key</key>
<version>1.0</version>
</aruba>
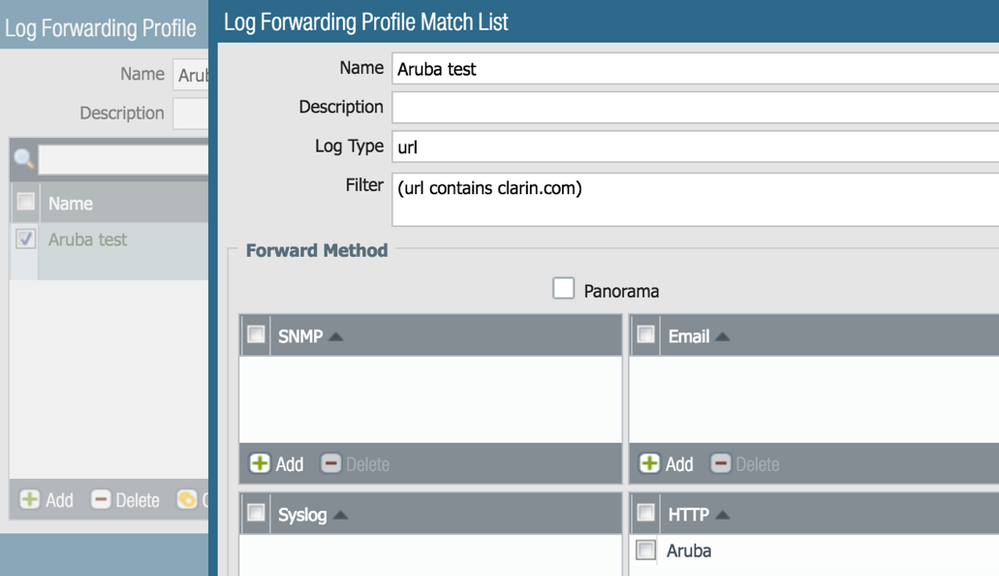
- Create a Log Forwarding Profile with a match list and select the HTTP server profile created earlier.
- Create a filter and assign it to the Log Forwarding Profile. In the example I have used a URL match to simplify the testing. Once it is working you can define an appropriate filter to match what is required on your environment.
- Apply the log forwarding profile to the rule/s that allow traffic from the wireless network
Aruba Instant Access Point Configuration Steps
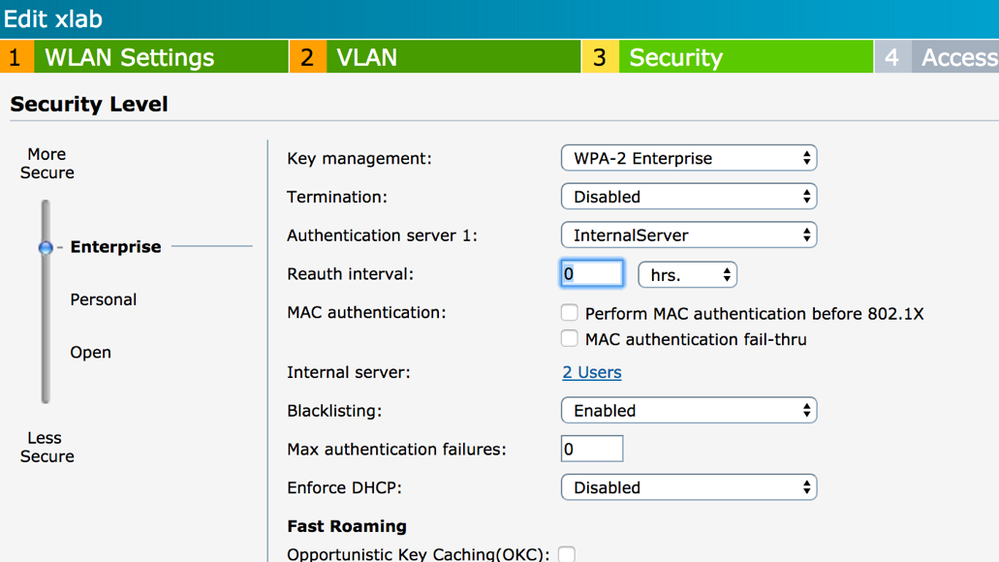
- Follow Aruba instructions to get a working IAP with at least one SSID
- Enable Blacklisting on the SSID
- Configure the XML API server from More – Services – Network Integration, using the firewall management IP address and the shared-key. The Palo Alto Network firewall integration is optional and not required (but recommended)
- Configure the blacklisting timeouts
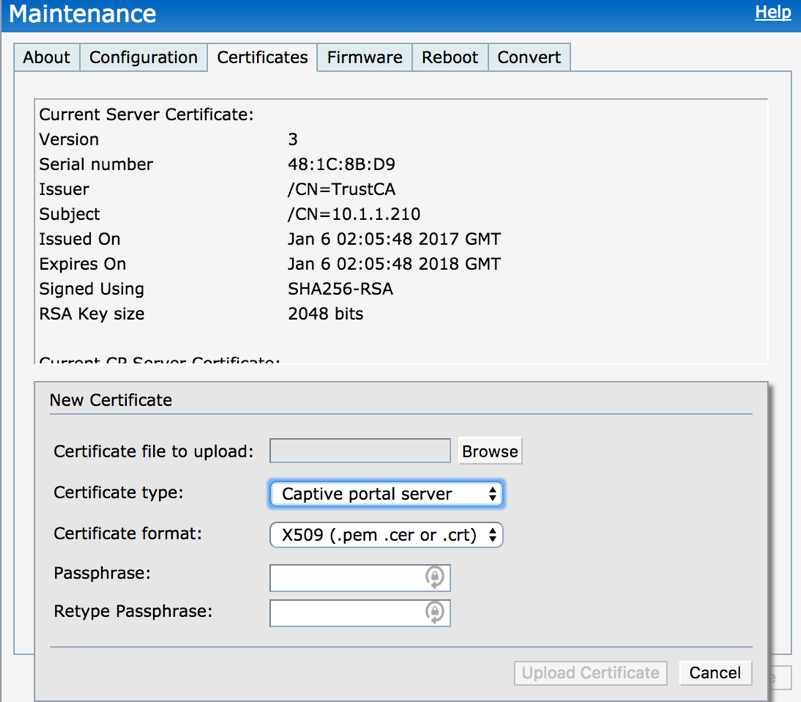
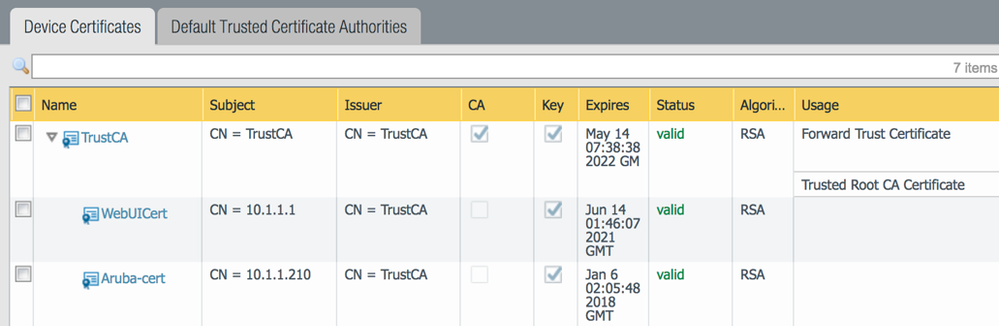
- Assign a certificate to the IAP captive portal that is trusted by the firewall (you can create a trusted CA in the firewall and generate the certificate for the IAP)
Testing the Integration
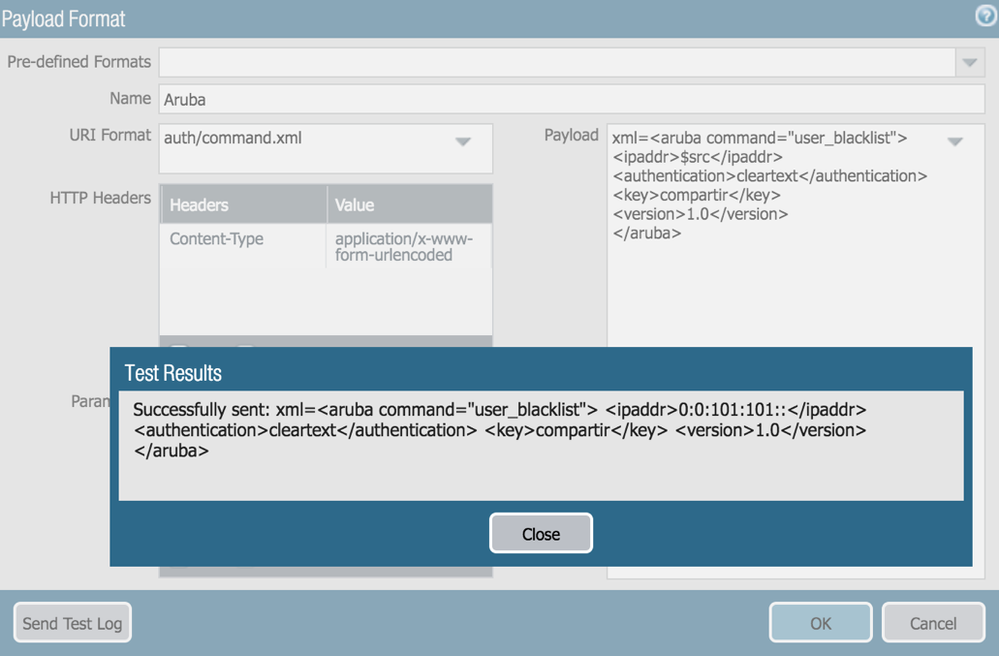
- You can send a test log from the http server profile payload format definition
- $src won’t resolve to the actual source IP address, but $src can be manually replaced with a testing client IP (a commit is required before sending the test log)
- A blacklisted client is immediately disconnected from the wireless and it will show under Info
Created by Mauricio Sabena
- 21732 Views
- 0 comments
- 0 Likes
-
Automation
1 -
HTTP
2 -
ifttt
1 -
Log Forwarding
4 -
NGFW Configuration
1 -
notifications
1 -
PAN-OS
2 -
Panorama Configuration
1 -
slack
1 -
twilio
1