- Access exclusive content
- Connect with peers
- Share your expertise
- Find support resources
Click Preferences to customize your cookie settings.
Unlock your full community experience!
Nominated Discussion: Tracing External IPs Back to Internal IPs at a Specific Time
- LIVEcommunity
- Articles
- General Articles
- Nominated Discussion: Tracing External IPs Back to Internal IPs at a Specific Time
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Printer Friendly Page
This article is based on a discussion, Tracing external IPs back to internal IPs at a specific moment in time..., posted by @Tom_Access. Read on to see the solution and collaboration from Cyber Elite @OtakarKlier & @Adrian_Jensen!
In the course of tracking down security vulnerabilities, I find myself trying to trace External IPs (from external security scan reports) back to Internal IPs at a specific moment in time (the timestamp from the scan report). Most of the time, it's very simple, as many internal IPs are NAT'd 1-to-1 to external IPs. Those tend to stay static. But there are also large groups of PAT'd addresses, such as whole ranges of internal IPs (like guest WiFi network DHCP pools) that go out a single external IP.
I'm really struggling with how to track these devices down. I can rarely even find a matching internal IP for that timestamp.
Is there a specific NAT/PAT log I can reference? Or a tool for this that I'm missing? I've been trying to use the traffic logs, but that's not always fruitful and it is tedious.
Any suggestions? I'm using a Palo Alto PA-5250 running PanOS 10.2.0.
Thanks in advance,
Tom
Solution:
First thing is to make sure you have logging at session end enabled on all of your security policies. Then you go into the Unified log and filter on source IP of the attacker. This should show all the traffic from that IP address. Then click on the paper/magnifying glass icon on the far left of the log.
This will bring up all the session details and will show you the NAT'd IP.
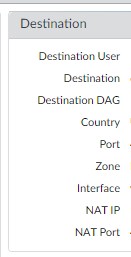
In addition the Monitor -> Logs -> Traffic viewer has many additional fields which can be selected/filtered upon by selecting the down arrow in the column name header and selecting additional fields. (Note: You can also reorder columns by dragging them to either side.)
Two additional columns that are not shown by default are "NAT Source IP" and "NAT Dest IP" (as well as NAT Source/Dest Port), which show the NAT'd IP results. You can filter you traffic on these fields as well. So, for instance, if you external security report complains about an exploit attempt from your public IP to an internet IP:
2022-07-08 12:35 - 1.2.3.4:53219 -> 5.6.7.8:443
You can find all the matching outbound traffic logs with a Traffic log filter like:
( natsrc eq 1.2.3.4 ) and ( natsport eq 53219 ) and ( addr.dst in 5.6.7.8 ) and (port.dst eq 443)
You can further add time filters to narrow down a window, though be aware that while log receive time appears to be a log database index, session start time is not. So queries using start time may take much longer/time out when searching (you can work around this by also using a wide receive time filter to pre-narrow the results subsequently filtered by the start time filter).
... and (receive_time geq '2022/07/08 12:30) and (receive_time leq '2022/07/08 12:50) and (start_time geq '2022/07/08 12:30)
- 10.2
- 10.2.0
- external IPs
- internal IPs
- logging
- Logs
- Network Security
- NGFW
- PA-5250
- Pan-os
- Reporting and Logging
- security policies
- Security Policy
- Traffic
- 4300 Views
- 0 comments
- 0 Likes
- Custom Signatures With ChatGPT and AI Security in General Articles
- Nominated Discussion: Configure Split Tunneling by Domain in General Articles
- Nominated Discussion - Sorting Question in General Articles
- Nominated Discussion: Using the REST API to Create a Bunch of Address Objects in General Articles
- A Guide to NAT on Palo Alto Networks Firewalls in Support FAQ
-
"Address Objects"
1 -
10.0
1 -
10.1
1 -
10.2
2 -
ACC
1 -
Active-Passive
1 -
AD
1 -
address objects
1 -
admin roles
1 -
Administration
6 -
Administrator Profile
1 -
ADNS
1 -
Advanced DNS Security
1 -
Advanced URL Filtering
2 -
Advanced WildFire
1 -
AI
2 -
AI Security
1 -
AI Threat
1 -
AIOPS
1 -
Ansible
1 -
antivirus
1 -
API
1 -
App-ID
1 -
applications
2 -
APS
1 -
Artificial Intelligence
1 -
Asset Management
1 -
Authentication
6 -
Authentication Profile
1 -
Authentication Sequence
1 -
automatically acquire commit lock
1 -
Automation
3 -
aws
3 -
Basic Configuration
4 -
Beacon
1 -
Best Practices
6 -
Block List
1 -
categories
1 -
certificates
1 -
Certification
1 -
Certifications
1 -
Certifications & Exams
1 -
CLI
5 -
CLI command
3 -
Cloud Automation
1 -
Cloud Identity Engine
1 -
cloud ngfw
1 -
cloud security
1 -
Collector Group
1 -
Commit and Push
1 -
Commit Process
1 -
Configuration
8 -
Configuration and Management
3 -
Configure Next Generation Firewall
1 -
console
1 -
Cortex
1 -
Cortex Data Lake
2 -
Cortex XDR
3 -
CPSP
1 -
Custom Signatures
3 -
cyber elite
1 -
cyberelite
11 -
Cybersecurity
1 -
dag
1 -
DDoS
1 -
Debug
1 -
debugging
2 -
Default Policy
1 -
discussions
1 -
DLP
1 -
EDL
2 -
education
1 -
Education and Training
1 -
Education Services
1 -
Educational Services
1 -
Effective Routing
1 -
End to End Encryption
1 -
Endpoint
1 -
export
1 -
failover
1 -
FAQ
1 -
file upload
1 -
Filtering
2 -
Firewall
2 -
Firewall VM-Series
2 -
Focused Services
3 -
Focused Services Proactive Insights
2 -
gateway
1 -
Gateway Load Balancer
2 -
GCP
2 -
GCP Firewall
1 -
geolocation
1 -
Getting Started
1 -
GitHub
1 -
Global Protect
1 -
Global Protect Cookies
1 -
GlobalProtect
7 -
GlobalProtect App
1 -
globalprotect gateway
1 -
GlobalProtect Portal
2 -
google
2 -
Google Cloud
3 -
google cloud platform
2 -
Hardware
2 -
Header Insertion
1 -
High Availability
1 -
How to
1 -
HTTP
1 -
https
1 -
Hybrid Cloud
1 -
ike
3 -
import
1 -
Installation & Upgrade
1 -
IoT
1 -
IPSec
4 -
IPSec VPN Administration
1 -
kerberos
1 -
Layer 2
1 -
Layer 3
1 -
Learning
1 -
licenses
1 -
local user
3 -
Log Cluster Design
1 -
Log Collection
3 -
Log Collector Design
2 -
Logging
1 -
login
1 -
Logs
3 -
Management
8 -
Management & Administration
5 -
MFA
1 -
Microsoft
1 -
Microsoft 365
1 -
Migration
1 -
minemeld
4 -
multi factor authentication
1 -
multi-factor authentication
1 -
multi-vsys
1 -
NAT
1 -
NetSec
1 -
NetSec Newsletter
1 -
network security
34 -
Network Security Management
1 -
Network-Security
1 -
Networking
1 -
newsletter
2 -
Next Generation Firewall
4 -
Next-Generation Firewall
42 -
next-generation firewall. network security
1 -
Next-Generation Firewall. NGFW
6 -
NGFW
30 -
NGFW Configuration
11 -
NGFW Newsletter
1 -
Nominated Discussion
1 -
Objects
2 -
OTP
1 -
PA-3200 Series
1 -
PA-400
1 -
pa-440
2 -
PA-5400 series
1 -
PA-800 Series
1 -
pa-820 firewall
1 -
Packet Buffer
1 -
packet debug
1 -
packet diag
1 -
PAN-OS
16 -
PAN-OS 10.2
1 -
PAN-OS 11.0
1 -
PAN-OS Prisma Access
1 -
Panorama
11 -
Panorama Configuration
2 -
PBF
1 -
PCNSA
1 -
PCNSE
1 -
performance
2 -
policies
2 -
policy
3 -
Policy Based Forwarding
1 -
Prisma Access
7 -
Prisma AIRS
1 -
Prisma SASE
2 -
Prisma SD-WAN
1 -
proactive insights
2 -
Prompt Poaching
1 -
Radius
1 -
Ransomware
1 -
RBI
2 -
region
1 -
Registration
1 -
Remote Browser Isolation
3 -
reporting and logging
1 -
RestAPI
1 -
Risk Management
1 -
Routing
1 -
SAML
1 -
SASE
1 -
script
2 -
SD WAN
1 -
SDWAN
1 -
Search
1 -
Security Advisory
1 -
Security automation
1 -
security policy
4 -
security profile
1 -
Security Profiles
2 -
Selective Push
1 -
Session Packet
1 -
Setup & Administration
8 -
Site-to-Site VPN
1 -
Split Tunneling
2 -
SSL
1 -
SSL Decryption
2 -
SSL Forward Proxy
1 -
SSO
1 -
Strata Cloud Manager
1 -
Strata Logging Service
2 -
Support Guidance
1 -
syslog
1 -
system modes
1 -
Tag
2 -
tags
2 -
Terraform
2 -
Threat
1 -
threat log
1 -
Threat Prevention
1 -
Threat Prevention License
1 -
Tips & Tricks
1 -
TLS
1 -
traffic_log
1 -
Traps
1 -
Troubleshoot
2 -
Troubleshoot. logs
1 -
Troubleshooting
6 -
tunnel
2 -
Tutorial
2 -
Unified Monitoring
1 -
upgrade
1 -
upgrade-downgrade
2 -
url categories
1 -
URL Filtering
2 -
URL-Filtering
1 -
User ID Probing
1 -
User-ID
1 -
User-ID & Authentication
1 -
User-ID mapping
1 -
userid
1 -
VM Series
1 -
VM-Series
7 -
VM-Series on AWS
3 -
VM-Series on GCP
2 -
VPC Flow logs
1 -
VPN
3 -
VPNs
4 -
Vulnerability
2 -
Vulnerability Protection
1 -
WhatsApp
1 -
WildFire
2 -
Wildfire License
1 -
wmi
1 -
XDR
1 -
xml
2 -
XML API
2
- Previous
- Next